Beginners Guide To The Google Search Engine
As a Digital Marketing Manager, I am not often asked the question what is Google? But I have lost count of a number of times I am asked how does Google work? A large proportion of the earth’s population who have internet access will know what Google is, however, the question should be ‘who’ are Google? The fact many people say ‘what’ instead of ‘who’ is testament to the enormous growth this company has undertaken over the years. So much so that the brand, Google, has now become a verb for almost all internet surfers – To search on the internet is now ‘To Google’. Google can nowadays be considered to be 3 things. 1) A Company. 2) A Brand. 3) A Search Engine.
What/Who are Google?
Back in 1995, Stanford university student Sergey Brin met his future business partner Larry Page when assigned the task to show Larry around the campus. Little did the two know that this first chance meeting was to be the very start of an extraordinary journey together. At first, the pair didn’t seem to agree on much, but over time the two struck up a partnership. One thing they did agree on was that there was a problem with how resources on the world wide web were sorted and ordered and set out to build a better search engine experience to offer a more enjoyable, useful and faster user experience. Initially, the company was set up under the name Backrub but was soon renamed Google. The term Google is a mathematical term to express ‘1’ followed by 100 ‘0’s’. The term aptly reflected the pair’s mission to organise resources within the world wide web.
Today, Google is much more than a provider of the world’s largest search engine, however, for the purposes of this article, we will be focusing our attention here.
What Is A Search Engine?
A search engine indexes web pages within the world wide web that are submitted to its index.
Definition of Index. In the world of search engines, in particular, Google, the index is the database where all the information Google retrieves from when it crawls a website is stored. Indexing is the process of collecting, parsing, and storing the data.
Instead of shelving books like a library would do, a search engine takes the individual pages from websites and indexes. This means it returns individual pages within its search results as opposed to the whole website. This provides a more granular result. There are, generally speaking, two ways in which a website can become indexed by a search engine. The first is for the website to be manually submitted to the search engine and the second, is for a website already within the search engines index to link to it.
Definition of A link. The term has been shortened from hyperlink. A hyperlink is a way of connecting an image or text within one web page to another web page. Hyperlinks can be recognised within a page. When a link is hovered over the browsers mouse pointer turns to a pointing finger.
The Face Of The Google Search Engine
The front end of a search engine has changed dramatically over the years, however, Google has worked hard over the years at simplifying the search process a user takes when looking for information and the way in which it presents results of information that assist in answering the searcher’s query. The front end of the Google search engine consists of two page templates. The first is the initial search page where you enter your search query. Generally speaking, this page contains the Google logo and a search box for you to enter the text of your search query along with a button that once clicks initiates the search.Asides from this you may find the odd text link but generally speaking Google aims to keep this page as minimalist as possible. The second page template you will see is the search engine results page (often referred to as a SERP or the SERPS.)
The Anatomy Of A Google Search Results Page
The Google search results page lists the results Google believes provide the information the searcher is looking for based on the search query they have entered. There are two types of results provided, organic search results and paid ads. Organic search results look similar to paid ads (through the Google Adwords advertising program) however paid ads are distinguishable by an ad symbol with slight alterations to formatting and character limits. Organic search results can appear in a few different formats, to date these appear as;
- Default organic result
- Social listing
- News listing
- Image listing
- Video listing
- Local pack listing
- App listings
- Rich snippet/rich answer listings
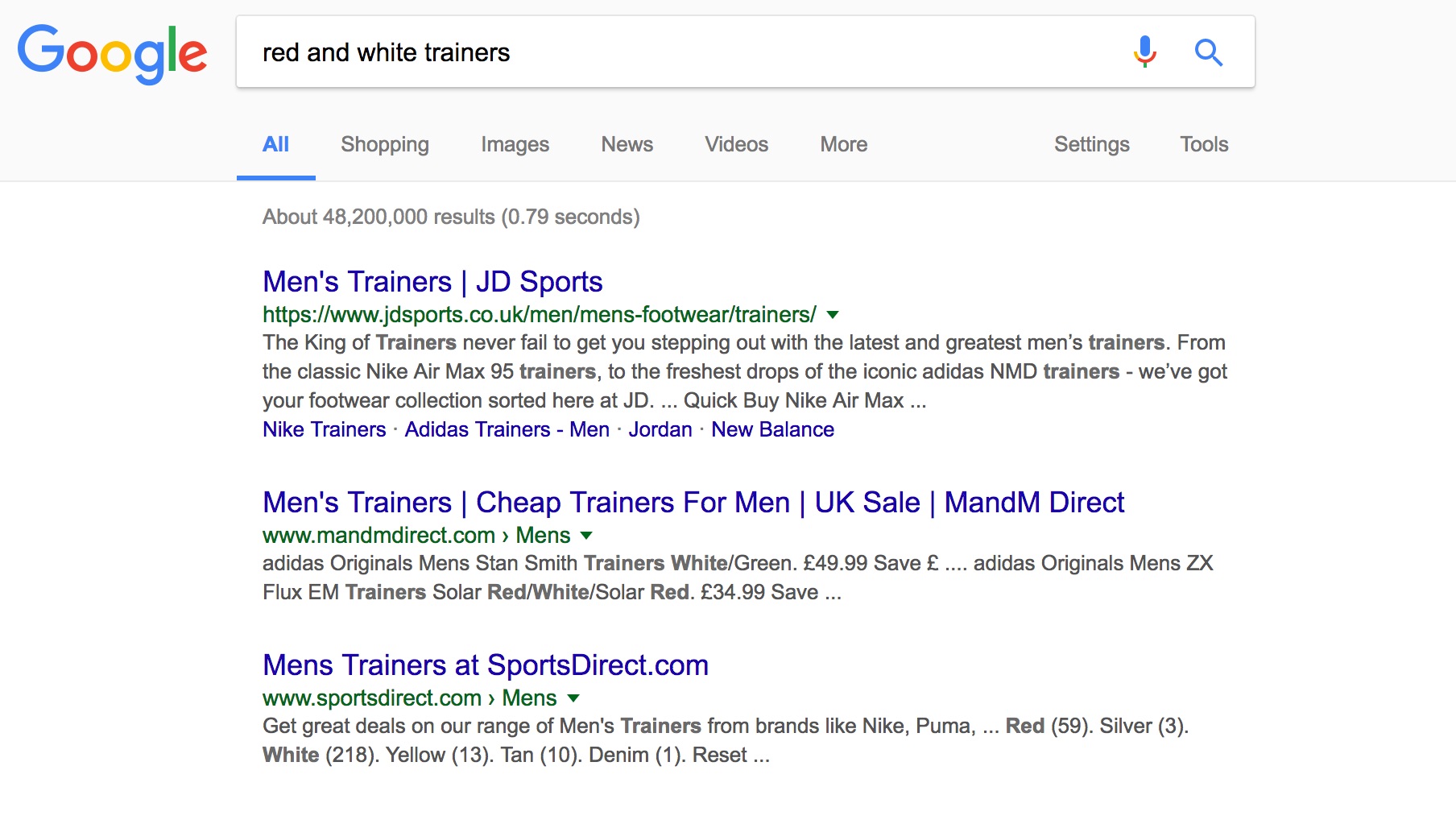
Default organic search listing example
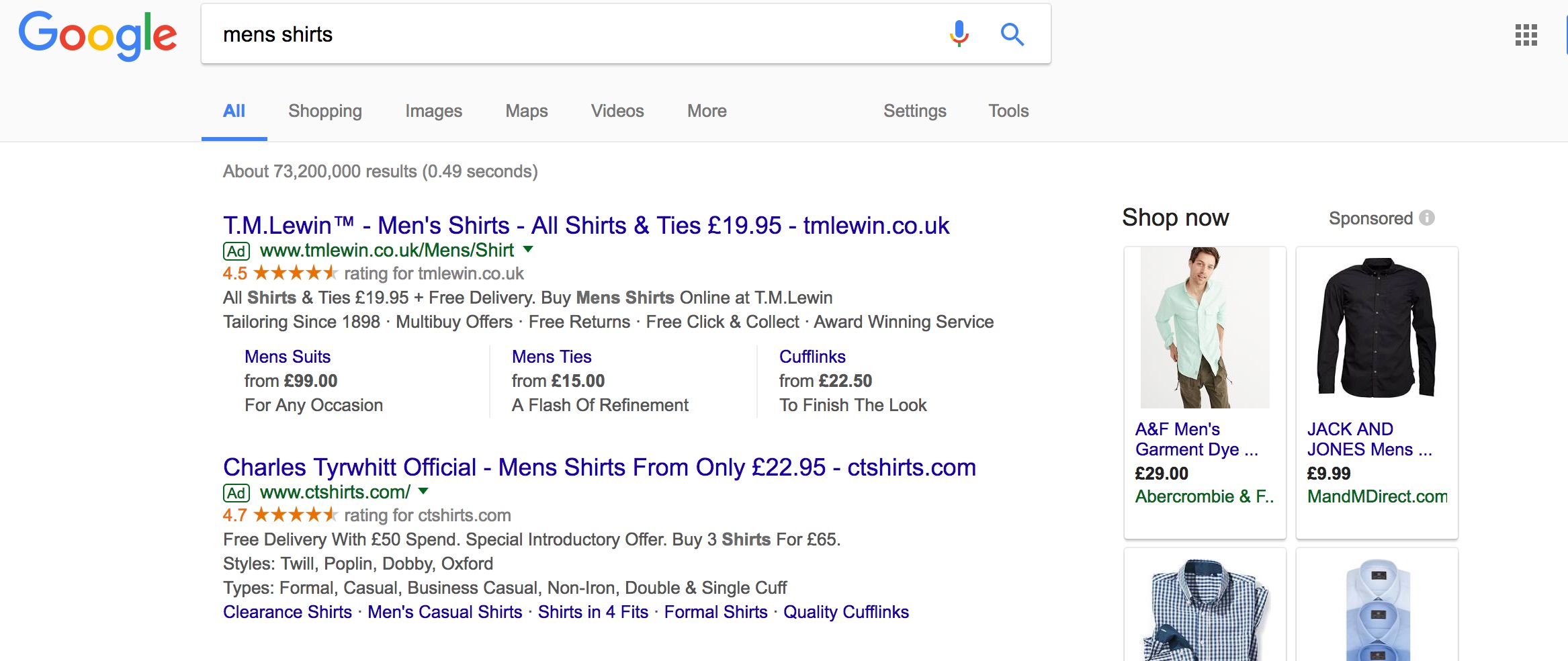
Paid ads appear in the Google search results through the following formats;
- Default Google Adwords text ad result
- Google Adwords Shopping result
Google Adwords paid ads examples (text ads & shopping ads)
Google returns the results of your search query in less than 1 second. Google has to search its database of data that stores all of the data from its most recent crawl of websites (which is huge, like trillions of web pages huge), organise the data in a results fashion, rank the results based on what it thinks is the most relevant answer first and then display these results (and it could be returning millions of results). This is lightning fast speed! There are also other processes that it must take before returning results such as personalisation. Google will attempt to personalise your results to additionally increase the relevancy of your results such as returning local results for location-based search queries.
How Does The Google Search Engine Work?
As search engines have changed over the years, it is now easier to talk about what the Google search engine is, and what it’s objectives are.
The Google search engine has two main functions, 1) collect data from web pages and sort web page data in an organised fashion within an index. 2) Using a complex algorithm to return the most relevant results from this index to a user based on content of their search query. The most relevant results show at the top of the search engine results page.
So the first job of the search engine is to collect the data. To do this, it uses search engine spiders, also known as bots, search bots or crawlers. The search engine spider is a program that finds web pages within an index or indexes connected by a network or networks. These search bots collect data from the search engines database of indexed pages. Google then uses this data to form a listing of results in reaction to a user’s Google search. The crawling bots are programmed to look in certain areas of a web page codes for certain data and will navigate through pages of a website through hyperlinks. Google decides what information the crawling bots look for which is decided by the ranking factors of its large algorithm.
Definition of an Algorithm. An algorithm by definition is a set of steps that need to be followed in a particular order in order to achieve a particular objective. A very simple algorithm could be a set of steps that need to be taken in order to achieve the desired cake. If the steps were not taken in a particular order the cake would not look and taste how it was intended. A search engine algorithm is a list of steps that a search engine crawling bot must take in order to retrieve certain data from a web page. Google’s algorithm can be dissected and a detailed explanation of Google’s algorithm can be found in the next section of this article.
Google’s Ranking Algorithm
Ever wondered why certain results in the Google search engine results page appear higher up on the page than others? The results you see have been selected and ordered (ranked) by Google based on the factors of its algorithm. In fact there is not just one algorithm, but a series of them. Over the years Google’s algorithm has grown in terms of number of factors and general complexity. In its infancy only a small handful of factors existed and these could easily be manipulated by website owners or search engine marketers in order to gain higher positions in search results pages by initially appearing to be more relevant to the search query than they actually were.
When you perform a search query, for example, ‘Where can I buy red trainers?’ Google has a huge index of web pages that contains the words ‘red trainers’. However, Google doesn’t want to return millions of results and in any order. It wants to return relevant results and do so in a fashion that presents you with the most relevant results first. So to do this Google must analyse the web page using factors from its algorithm. Google has never released its algorithm into the public domain so the factors and their individual importance in ranking search results is down to interpretation. Over the years Google has dropped hints and even clarified that certain elements of a website are focused on by its algorithm. Over time, Google refines its algorithm. At some points it makes quite significant alterations and at other times it is more of a case of fine tuning.
Amongst the search engine marketing community it is often concluded that there are over 200 ranking signals/factors within Google’s search algorithm and it is believed, again amongst the community, that Google makes around 500-600 alterations to its algorithm every year. We know Google’s algorithm looks at two decisive areas, on page (elements that appear on a web page) and off page (outside influences on the web page in question). Below we have listed some 3 algorithm ranking factors examples that we, and a large portion of the community, believe to be influential.
- Keywords in search query matching content within web page (this doesn’t mean a page that contains a repetition of the same word will score big points here. Google’s search algorithm is semantic search model. This means it looks for words that group together into a common theme such a main word ‘football’. Other words that fit into the semantic theme: liverpool football club, stadium, fans, boots, goal.
- Keywords in search query matching content within the meta title of the web page.
Links from other web pages to the webpage it is analysing. Not just any link though. If the link comes from a page containing similar content the value of this link increases. Links from one web page to another are seen by Google’s algorithm as a vote of confidence. The theory of hyperlinking from one web page to another, is to point the user to a source of information that will be useful to them when reading the content of your webpage. Maybe another web page contains more useful information on a particular subject that you are not skilled enough to talk about? In that case, a link within your content to another page where a user can find this information is useful both to the visitor and Google. - Social Signals. Social media websites seem to be having a growing influence in the Google search algorithm.
Search engine news company, Search Engine Land, produced a periodic table of all the SEO ranking factors it believed to be influential in Google’s ranking algorithm a few years back. It has since been updated and recently they released their fourth edition. We covered this in our Month in Search article back in June, which contains links to the original source information where the table can be downloaded.
Remember, the factors that make up Google’s algorithm and what we as search marketers believe they are may not be 100% accurate; although through lots of experiments and data analysis, the general census is that it isn’t far off.
How Google improves its algorithm and how often it changes
Was Google the first search engine?
Search engines have come a long way and so have the goals they set out to achieve. Google has been a part of our lives for so long now, it is hard to imagine there was much before this. Young generations of today may be easily forgiven thinking Google was the first search engine, however, there were many predecessors. The first search engine is often considered to be the Archie search engine; although it may not be recognised in quite the same way as Google is today. Archie started as project at the McGill University School of Computer Science back in 1987. A select party of students and staff, mainly volunteers, were tasked with finding a solution that could connect the school to the internet. Remember, this is way before Bing, Ask.com and Yahoo were formed so back then this was quite a substantial task. In its rawest form the first search engine was simple, but did exactly what was asked of it. Archie would contact a list of FTP archives every so often (approximately once a month) and then store information in local files.
Definition of FTP. An acronym that stands for file transfer protocol, a protocol used for transferring files between different computers connected to the same network.
There have been many search engines that have come and gone along the way. Google launched in 1998 and prior to that, search engines were launched by recognisable companies such as Yahoo, Lycos and Ask Jeeves. Since 1998, there have been lots of companies who have launched search engine products, some have failed and some are still trading today. The most successful ones are generally those who exist in countries where Google is banned, mostly for political reasons. At the date of this publication, Google’s global share in the search engine market is around 80%. In my eyes they would need to do something seriously wrong to lose their majority share of this market and would only probably do so through their own downfall, something I cannot see happening in my lifetime.
How can I make my website more visible in Google?
In order to make your web pages rank in Google search results for certain keywords or search phrases, you need to optimise your website, taking into consideration the factors of Google’s ranking algorithm. This is both an art and a science, one you can teach yourself or invest in a search engine optimisation campaign from a skilled, professional agency. No matter which option you choose, search engine optimisation requires a lot of time and effort; however, the results can be very lucrative. Here at Verve we plan, develop and manage search engine optimisation campaigns focused on profitable return on investment for e-commerce and brochure websites. To chat with our search engine optimisation specialists about a potential new campaign or for a review of your existing campaign contact our search engine optimisation team.
Resources
https://www.google.com/intl/en/about/our-story/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_web_search_engines
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_search_engine#History
http://searchengineland.com/seotable
https://www.google.com/search/howsearchworks/algorithms/
https://www.netmarketshare.com/search-engine-market-share.aspx?qprid=4&qpcustomd=0

